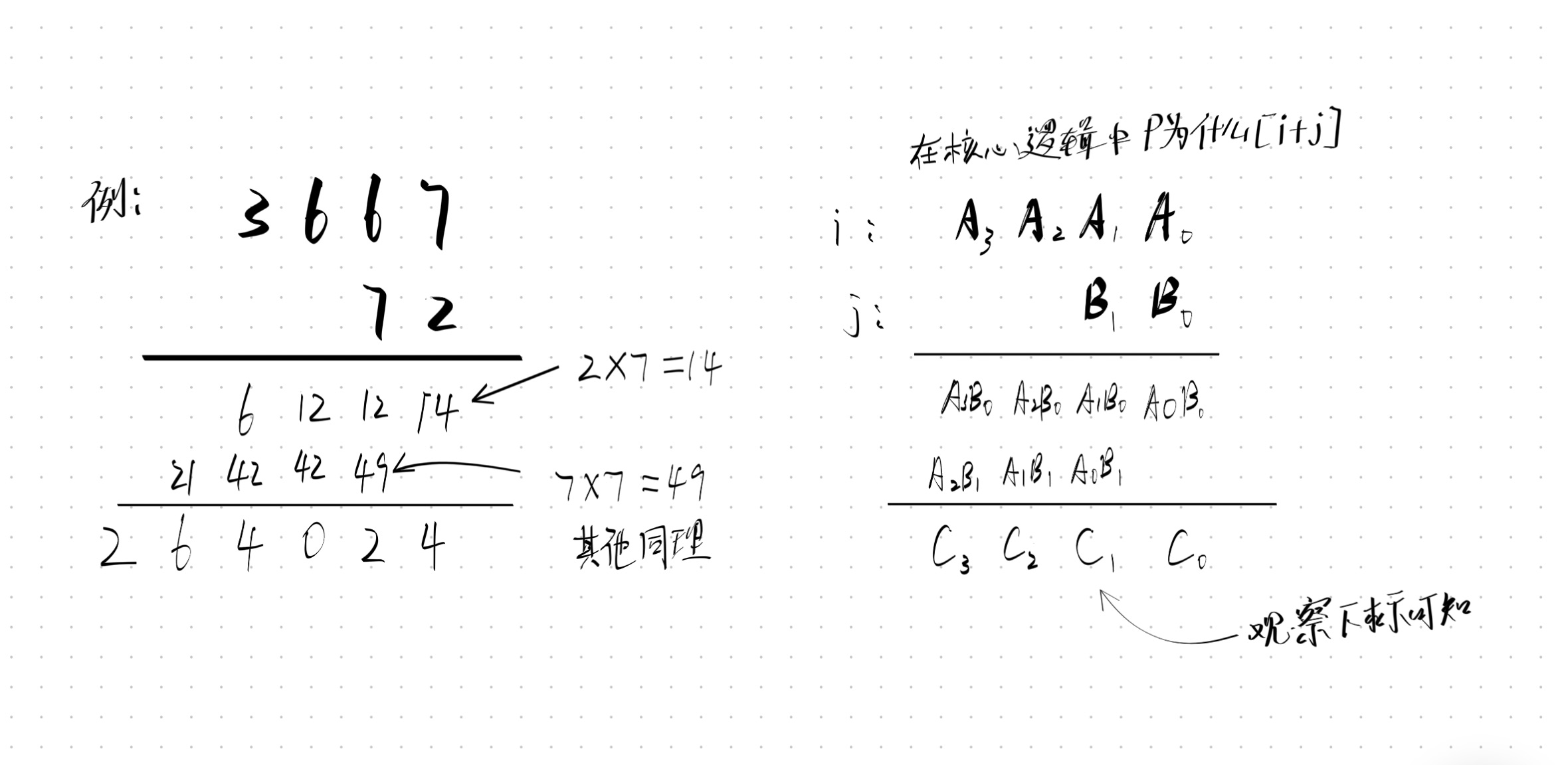
搜索到
17
篇与
的结果
-
 离散化 为什么要离散化处理? 数据过于多时难以表示数组下标 离散化是什么? 可以类比哈希表离散化就像哈希一样,只不过是由大映射到小。 比如你有一个长度为1e9数列,其中大部分值都为0,而你要寻找某一区间和,1e9的长度开数组肯定会爆栈,所以我们需要把有效区间缩小至小区间内表示。离散化例题 ac代码:#include <bits/stdc++.h> using ll = long long; const int N = 3e5 + 9; std::vector<int> X; ll a[N]; // 操作和询问 struct Q { ll a, b; } add[N], que[N]; int getindex(ll x) { return std::lower_bound(X.begin(), X.end(), x) - X.begin() + 1; } void vol() { int n, q; std::cin >> n >> q; // 离线处理 for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) { ll x, w; std::cin >> x >> w; X.push_back(x); add[i] = {x, w}; } for (int i = 1; i <= q; i++) { ll l, r; std::cin >> l >> r; X.push_back(l), X.push_back(r); que[i] = {l, r}; } // 排序去重 std::sort(X.begin(), X.end()); X.erase(std::unique(X.begin(), X.end()), X.end()); for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) { // 由大到小 int x = getindex(add[i].a); ll w = add[i].b; a[x] += w; } // 前缀和 for (int i = 1; i <= X.size(); i++) { a[i] += a[i - 1]; } for (int i = 1; i <= q; i++) { int l = getindex(que[i].a); int r = getindex(que[i].b); std::cout << a[r] - a[l - 1] << "\n"; } } int main() { std::ios::sync_with_stdio(0), std::cout.tie(0), std::cin.tie(0); int t; t = 1; //std::cin >> t; while (t--) { vol(); } return 0; }
离散化 为什么要离散化处理? 数据过于多时难以表示数组下标 离散化是什么? 可以类比哈希表离散化就像哈希一样,只不过是由大映射到小。 比如你有一个长度为1e9数列,其中大部分值都为0,而你要寻找某一区间和,1e9的长度开数组肯定会爆栈,所以我们需要把有效区间缩小至小区间内表示。离散化例题 ac代码:#include <bits/stdc++.h> using ll = long long; const int N = 3e5 + 9; std::vector<int> X; ll a[N]; // 操作和询问 struct Q { ll a, b; } add[N], que[N]; int getindex(ll x) { return std::lower_bound(X.begin(), X.end(), x) - X.begin() + 1; } void vol() { int n, q; std::cin >> n >> q; // 离线处理 for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) { ll x, w; std::cin >> x >> w; X.push_back(x); add[i] = {x, w}; } for (int i = 1; i <= q; i++) { ll l, r; std::cin >> l >> r; X.push_back(l), X.push_back(r); que[i] = {l, r}; } // 排序去重 std::sort(X.begin(), X.end()); X.erase(std::unique(X.begin(), X.end()), X.end()); for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) { // 由大到小 int x = getindex(add[i].a); ll w = add[i].b; a[x] += w; } // 前缀和 for (int i = 1; i <= X.size(); i++) { a[i] += a[i - 1]; } for (int i = 1; i <= q; i++) { int l = getindex(que[i].a); int r = getindex(que[i].b); std::cout << a[r] - a[l - 1] << "\n"; } } int main() { std::ios::sync_with_stdio(0), std::cout.tie(0), std::cin.tie(0); int t; t = 1; //std::cin >> t; while (t--) { vol(); } return 0; } -
 快速幂 快速幂 用于快速求a^b的算法 思想:拆分 例:求2^13 等价于求 2^1 2^4 2^8 其中13二进制表示(1101).对应十进制的位权为8,4,1. 因此对于求幂,我们可以将指数的二进制表示数每位所对应的十进制的位权作为拆分后的指数. 复杂度不难看出是O(logn).#include <iostream> int main () { int a, b; std::cin >> a >> b; long long ans = 1; while(b) { if(b & 1) { ans *= a; } a *= a; b >>= 1; } std::cout << ans; return 0; }
快速幂 快速幂 用于快速求a^b的算法 思想:拆分 例:求2^13 等价于求 2^1 2^4 2^8 其中13二进制表示(1101).对应十进制的位权为8,4,1. 因此对于求幂,我们可以将指数的二进制表示数每位所对应的十进制的位权作为拆分后的指数. 复杂度不难看出是O(logn).#include <iostream> int main () { int a, b; std::cin >> a >> b; long long ans = 1; while(b) { if(b & 1) { ans *= a; } a *= a; b >>= 1; } std::cout << ans; return 0; } -
 高精度运算(加减乘除) 在程序中高精度加法和高精度减法的运算本质是模拟我们在小学就学过的运算规则,也是我们平时用的运算规则:相加大于10就进1,相减小于就向高位借.高精度加法//高精度加法 #include <iostream> #include <string> #include <vector> #include <algorithm> //a,b字符串用于存入两个大数 std::string a, b; //m,n分别逆序存入a,b std::vector <int> m, n, p; //la,lb用于记录a,b的位数 int la, lb; void highPrecisionAddition() { int sum = 0; for (int i = 0; i < la || i < lb; i++) { if (i < la) { sum += m[i]; } if (i < lb) { sum += n[i]; } p.push_back(sum % 10); sum /= 10; } if (sum) { p.push_back(sum); } } int main() { //以字符串形式存放 std::cin >> a; std::cin >> b; la = a.size(); lb = b.size(); //将字符串按位逆序存入数组m, n for (int i = la - 1; i >= 0; i--) { m.push_back(a[i] - '0'); } for (int i = lb - 1; i >= 0; i--) { n.push_back(b[i] - '0'); } highPrecisionAddition(); reverse(p.begin(), p.end()); for (auto i : p) { std::cout << i; } return 0; }高精度减法//高精度减法 #include <iostream> #include <string> #include <vector> #include <algorithm> std::string a, b; std::vector <int> m, n, p; int la, lb; bool cmp() { if (la != lb) { return la > lb; } for (int i = la - 1; i >= 0; i--) { if (m[i] != n[i]) { return m[i] > n[i]; } } return true; } void highPrecisionSubtraction(std::vector <int> &m, std::vector <int> &n) { int sub = 0; for (int i = 0; i < la || i < lb; i++) { sub = m[i]; if (i < lb) { sub -= n[i]; } if (sub < 0) { m[i + 1]--; sub += 10; } p.push_back(sub); } //去除前面多余的零,保证输出时前面不出现零 while (p.size() > 1 && !p.back()) { p.pop_back(); } } int main () { std::cin >> a; std::cin >> b; la = a.size(); lb = b.size(); for (int i = la - 1; i >= 0; i--) { m.push_back(a[i] - '0'); } for (int i = lb - 1; i >= 0; i--) { n.push_back(b[i] - '0'); } //如果输入是小减大则需要输出负号 if (!cmp()) { //保证highPrecisionSubtraction里是大减小 std::swap(m, n); std::cout << "-"; } highPrecisionSubtraction(m, n); reverse(p.begin(), p.end()); for (auto i : p) { std::cout << i; } return 0; }高精度乘法 在程序中的高精度乘法也与我们平时的运算差不多,略有不同. //高精度乘法 #include <iostream> #include <string> #include <vector> #include <algorithm> std::string a, b; std::vector <int> m, n; int la, lb; void highPrecisionMultiplication(std::vector <int>& p) { for (int i = 0; i < la; i++) { for (int j = 0; j < lb; j++) { p[i + j] += m[i] * n[j]; p[i + j + 1] += p[i + j] / 10; p[i + j] %= 10; } } while (p.size() > 1 && !p.back()) { p.pop_back(); } } int main() { std::cin >> a; std::cin >> b; la = a.size(); lb = b.size(); std::vector <int> p(la + lb); for (int i = la - 1; i >= 0; i--) { m.push_back(a[i] - '0'); } for (int i = lb - 1; i >= 0; i--) { n.push_back(b[i] - '0'); } highPrecisionMultiplication(p); std::reverse(p.begin(), p.end()); for (auto i : p) { std::cout << i; } return 0; } 高精度除法 高精度除法的被除数为大数,而除数相对较小在整型范围内运算规则同平时在纸上所列的计算方法#include <iostream> #include <string> #include <vector> std::string a; int n; std::vector <int> m, p; int la, lb; void highPrecisionDivision() { long long r = 0; for (int i = la - 1; i >= 0; i--) { r = r * 10 + m[i]; p.push_back(r / n); r %= n; } while (p.size() > 1 && !p.back()) { p.pop_back(); } } int main () { std::cin >> a; std::cin >> n; la = a.size(); for (int i = la - 1; i >= 0; i--) { m.push_back(a[i] - '0'); } highPrecisionDivision(); for (auto i : p) { std::cout << i; } return 0; }
高精度运算(加减乘除) 在程序中高精度加法和高精度减法的运算本质是模拟我们在小学就学过的运算规则,也是我们平时用的运算规则:相加大于10就进1,相减小于就向高位借.高精度加法//高精度加法 #include <iostream> #include <string> #include <vector> #include <algorithm> //a,b字符串用于存入两个大数 std::string a, b; //m,n分别逆序存入a,b std::vector <int> m, n, p; //la,lb用于记录a,b的位数 int la, lb; void highPrecisionAddition() { int sum = 0; for (int i = 0; i < la || i < lb; i++) { if (i < la) { sum += m[i]; } if (i < lb) { sum += n[i]; } p.push_back(sum % 10); sum /= 10; } if (sum) { p.push_back(sum); } } int main() { //以字符串形式存放 std::cin >> a; std::cin >> b; la = a.size(); lb = b.size(); //将字符串按位逆序存入数组m, n for (int i = la - 1; i >= 0; i--) { m.push_back(a[i] - '0'); } for (int i = lb - 1; i >= 0; i--) { n.push_back(b[i] - '0'); } highPrecisionAddition(); reverse(p.begin(), p.end()); for (auto i : p) { std::cout << i; } return 0; }高精度减法//高精度减法 #include <iostream> #include <string> #include <vector> #include <algorithm> std::string a, b; std::vector <int> m, n, p; int la, lb; bool cmp() { if (la != lb) { return la > lb; } for (int i = la - 1; i >= 0; i--) { if (m[i] != n[i]) { return m[i] > n[i]; } } return true; } void highPrecisionSubtraction(std::vector <int> &m, std::vector <int> &n) { int sub = 0; for (int i = 0; i < la || i < lb; i++) { sub = m[i]; if (i < lb) { sub -= n[i]; } if (sub < 0) { m[i + 1]--; sub += 10; } p.push_back(sub); } //去除前面多余的零,保证输出时前面不出现零 while (p.size() > 1 && !p.back()) { p.pop_back(); } } int main () { std::cin >> a; std::cin >> b; la = a.size(); lb = b.size(); for (int i = la - 1; i >= 0; i--) { m.push_back(a[i] - '0'); } for (int i = lb - 1; i >= 0; i--) { n.push_back(b[i] - '0'); } //如果输入是小减大则需要输出负号 if (!cmp()) { //保证highPrecisionSubtraction里是大减小 std::swap(m, n); std::cout << "-"; } highPrecisionSubtraction(m, n); reverse(p.begin(), p.end()); for (auto i : p) { std::cout << i; } return 0; }高精度乘法 在程序中的高精度乘法也与我们平时的运算差不多,略有不同. //高精度乘法 #include <iostream> #include <string> #include <vector> #include <algorithm> std::string a, b; std::vector <int> m, n; int la, lb; void highPrecisionMultiplication(std::vector <int>& p) { for (int i = 0; i < la; i++) { for (int j = 0; j < lb; j++) { p[i + j] += m[i] * n[j]; p[i + j + 1] += p[i + j] / 10; p[i + j] %= 10; } } while (p.size() > 1 && !p.back()) { p.pop_back(); } } int main() { std::cin >> a; std::cin >> b; la = a.size(); lb = b.size(); std::vector <int> p(la + lb); for (int i = la - 1; i >= 0; i--) { m.push_back(a[i] - '0'); } for (int i = lb - 1; i >= 0; i--) { n.push_back(b[i] - '0'); } highPrecisionMultiplication(p); std::reverse(p.begin(), p.end()); for (auto i : p) { std::cout << i; } return 0; } 高精度除法 高精度除法的被除数为大数,而除数相对较小在整型范围内运算规则同平时在纸上所列的计算方法#include <iostream> #include <string> #include <vector> std::string a; int n; std::vector <int> m, p; int la, lb; void highPrecisionDivision() { long long r = 0; for (int i = la - 1; i >= 0; i--) { r = r * 10 + m[i]; p.push_back(r / n); r %= n; } while (p.size() > 1 && !p.back()) { p.pop_back(); } } int main () { std::cin >> a; std::cin >> n; la = a.size(); for (int i = la - 1; i >= 0; i--) { m.push_back(a[i] - '0'); } highPrecisionDivision(); for (auto i : p) { std::cout << i; } return 0; } -
 素数筛法(埃氏筛法、线性筛法) 素数筛法:用于筛选出素数核心思想:用一个数筛选其余的数普通筛法:时间复杂度为O(nlogn)#include <iostream> #define N 100 bool vis[N] = { false };// 0到N-1的元素都没有被标记 int primes[N]; // 存放素数 int tot; //普通筛法 int main() { vis[0] = vis[1] = true; // 0和1不是素数 for (int i = 2; i < N; i++) { if (!vis[i]) { primes[++tot] = i; // 找到一个素数,存放到primes中 } for (int j = 2 * i; j < N; j += i) { vis[j] = true; // 将i的倍数都标记为已被筛掉 } } for (int i = 1; i < tot; i++) { std::cout << primes[i] << " "; } std::cout << std::endl; return 0; }继续优化的话可以 只用质数去筛 ,这也就是埃氏筛法:时间复杂度为:O(nloglogn)int main() { vis[0] = vis[1] = true; // 0和1不是素数 for (int i = 2; i < N; i++) { if (!vis[i]) { primes[++tot] = i; // 找到一个素数,存放到primes中 for (int j = i * i; j < N; j += i) { vis[j] = true; // 将i的倍数都标记为已被筛掉 } } } for (int i = 1; i < tot; i++) { std::cout << primes[i] << " "; } std::cout << std::endl; return 0; }继续优化 线性筛 : 每个数都被其最小的质因数筛掉 时间复杂度为O(n)int main() { vis[0] = vis[1] = true; for (int i = 2; i <= N; i++) { if (!vis[i]) { primes[++tot] = i; } for (int j = 1; i * primes[j] < N; j++) { vis[i * primes[j]] = true; if (i % primes[j] == 0) { break; } } } for (int i = 1; i < tot; i++) { std::cout << primes[i]<< " "; } std::cout << std::endl; return 0; }
素数筛法(埃氏筛法、线性筛法) 素数筛法:用于筛选出素数核心思想:用一个数筛选其余的数普通筛法:时间复杂度为O(nlogn)#include <iostream> #define N 100 bool vis[N] = { false };// 0到N-1的元素都没有被标记 int primes[N]; // 存放素数 int tot; //普通筛法 int main() { vis[0] = vis[1] = true; // 0和1不是素数 for (int i = 2; i < N; i++) { if (!vis[i]) { primes[++tot] = i; // 找到一个素数,存放到primes中 } for (int j = 2 * i; j < N; j += i) { vis[j] = true; // 将i的倍数都标记为已被筛掉 } } for (int i = 1; i < tot; i++) { std::cout << primes[i] << " "; } std::cout << std::endl; return 0; }继续优化的话可以 只用质数去筛 ,这也就是埃氏筛法:时间复杂度为:O(nloglogn)int main() { vis[0] = vis[1] = true; // 0和1不是素数 for (int i = 2; i < N; i++) { if (!vis[i]) { primes[++tot] = i; // 找到一个素数,存放到primes中 for (int j = i * i; j < N; j += i) { vis[j] = true; // 将i的倍数都标记为已被筛掉 } } } for (int i = 1; i < tot; i++) { std::cout << primes[i] << " "; } std::cout << std::endl; return 0; }继续优化 线性筛 : 每个数都被其最小的质因数筛掉 时间复杂度为O(n)int main() { vis[0] = vis[1] = true; for (int i = 2; i <= N; i++) { if (!vis[i]) { primes[++tot] = i; } for (int j = 1; i * primes[j] < N; j++) { vis[i * primes[j]] = true; if (i % primes[j] == 0) { break; } } } for (int i = 1; i < tot; i++) { std::cout << primes[i]<< " "; } std::cout << std::endl; return 0; } -
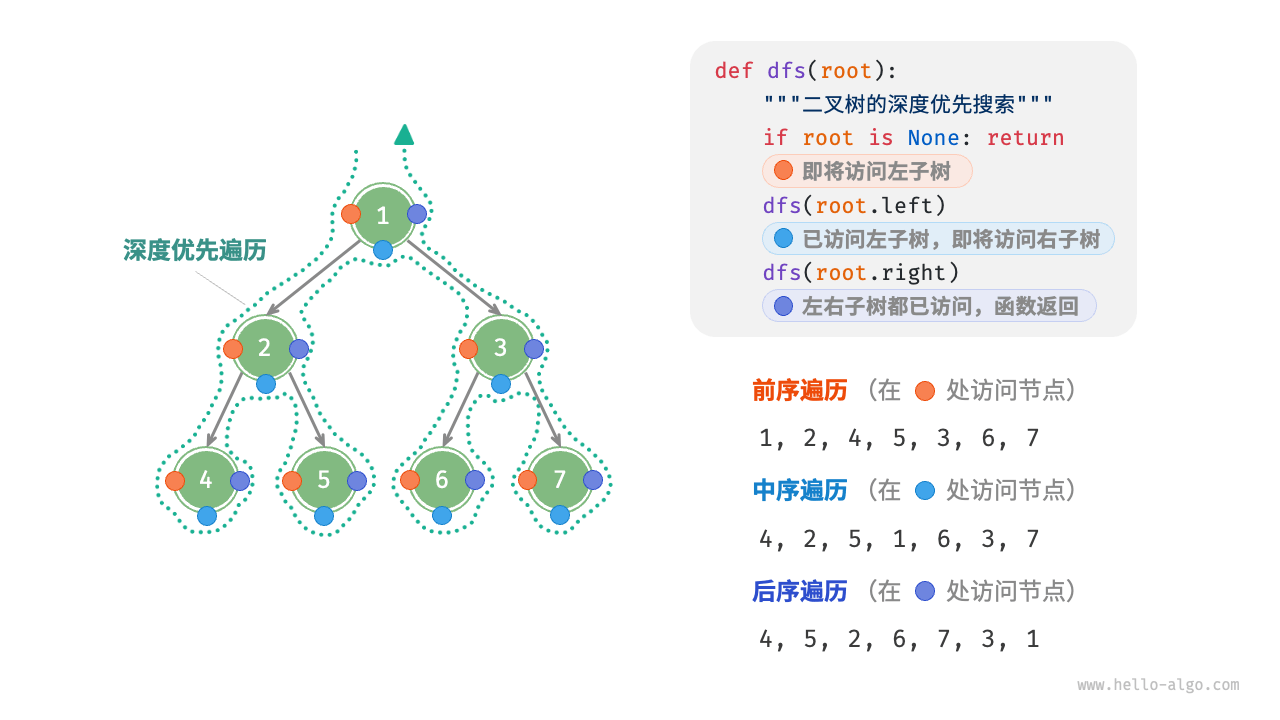
 二叉树的建立与遍历 二叉树是一种非线性数据结构. 二叉树 由节点构成,每个节点包含节点值和指向左节点和右节点的指针.常用术语: 根节点(root node):位于二叉树顶层的节点,没有父节点。叶节点(leaf node):没有子节点的节点,其两个指针均指向 None 。边(edge):连接两个节点的线段,即节点引用(指针)。节点所在的层(level):从顶至底递增,根节点所在层为 1 。节点的度(degree):节点的子节点的数量。在二叉树中,度的取值范围是 0、1、2 。二叉树的高度(height):从根节点到最远叶节点所经过的边的数量。节点的深度(depth):从根节点到该节点所经过的边的数量。节点的高度(height):从距离该节点最远的叶节点到该节点所经过的边的数量。二叉树的遍历 分为层序遍历,前序遍历,中序遍历,后序遍历.层序遍历本质为BFS,即广度优先搜索.层序遍历顾名思义,为一层层的从上往下,从左到右遍历.前序遍历,中序遍历,后序遍历本质为DFS,即深度优先搜索.访问时机如图: 代码示例:#include<vector> #include<queue> #include<iostream> struct tree{ int value; tree *left; tree *right; tree(int x) : value(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr){} }; std::vector<int> vec; //层序遍历 std::vector<int> levelorder(tree *root){ std::queue<tree *> q; q.push(root); std::vector<int> vec; while(!q.empty()){ tree *node = q.front(); q.pop(); vec.push_back(node->value); if(node->left != nullptr){ q.push(node->left); } if(node->right != nullptr){ q.push(node->right); } } return vec; } //前序遍历 void preorder(tree *root){ if(root == nullptr){ return; } vec.push_back(root->value); preorder(root->left); preorder(root->right); } //中序遍历 void inorder(tree *root){ if(root == nullptr){ return; } inorder(root->left); vec.push_back(root->value); inorder(root->right); } //后序遍历 void postorder(tree *root){ if(root == nullptr){ return; } postorder(root->left); postorder(root->right); vec.push_back(root->value); } int main(){ tree *t0 = new tree(1); tree *t1 = new tree(2); tree *t2 = new tree(3); tree *t3 = new tree(4); tree *t4 = new tree(5); t0->left = t1; t0->right = t2; t1->left = t3; t1->right = t4; preorder(t0); for(auto &i : vec){ std::cout << i << " "; } std::cout << std::endl; vec.clear(); inorder(t0); for(auto &i : vec){ std::cout << i << " "; } std::cout << std::endl; vec.clear(); postorder(t0); for(auto &i : vec){ std::cout << i << " "; } std::cout << std::endl; vec.clear(); return 0; }使用数组表示二叉树: 用数组表示时,观察可知节点下标为 i 时,父节点下标为 (i - 1) / 2 左节点下标为 2 i + 1 ,右节点下标为 2 i + 2 依此规律我们可以使用数组表示出二叉树#include<vector> #include<iostream> std::vector<int> vec; int parent(int i){ return (i - 1) / 2; } int left(int i){ return 2 * i + 1; } int right(int i){ return 2 * i + 2; } void pretree(std::vector<int> &tree, int i){ if(i < 0 || i >= tree.size()){ return; } vec.push_back(tree[i]); pretree(tree, left(i)); pretree(tree, right(i)); } void intree(std::vector<int> &tree, int i){ if(i < 0 || i >= tree.size()){ return; } intree(tree, left(i)); vec.push_back(tree[i]); intree(tree, right(i)); } void posttree(std::vector<int> &tree, int i){ if(i < 0 || i >= tree.size()){ return; } posttree(tree, left(i)); posttree(tree, right(i)); vec.push_back(tree[i]); } int main(){ std::vector<int> tree(10); for(int i = 0; i < 10; i++){ std::cin >> tree[i]; } pretree(tree, 0); for(auto &i : vec){ std::cout << i << " "; } std::cout << std::endl; vec.clear(); intree(tree, 0); for(auto &i : vec){ std::cout << i << " "; } std::cout << std::endl; vec.clear(); posttree(tree, 0); for(auto &i : vec){ std::cout << i << " "; } std::cout << std::endl; vec.clear(); return 0; }参考文章
二叉树的建立与遍历 二叉树是一种非线性数据结构. 二叉树 由节点构成,每个节点包含节点值和指向左节点和右节点的指针.常用术语: 根节点(root node):位于二叉树顶层的节点,没有父节点。叶节点(leaf node):没有子节点的节点,其两个指针均指向 None 。边(edge):连接两个节点的线段,即节点引用(指针)。节点所在的层(level):从顶至底递增,根节点所在层为 1 。节点的度(degree):节点的子节点的数量。在二叉树中,度的取值范围是 0、1、2 。二叉树的高度(height):从根节点到最远叶节点所经过的边的数量。节点的深度(depth):从根节点到该节点所经过的边的数量。节点的高度(height):从距离该节点最远的叶节点到该节点所经过的边的数量。二叉树的遍历 分为层序遍历,前序遍历,中序遍历,后序遍历.层序遍历本质为BFS,即广度优先搜索.层序遍历顾名思义,为一层层的从上往下,从左到右遍历.前序遍历,中序遍历,后序遍历本质为DFS,即深度优先搜索.访问时机如图: 代码示例:#include<vector> #include<queue> #include<iostream> struct tree{ int value; tree *left; tree *right; tree(int x) : value(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr){} }; std::vector<int> vec; //层序遍历 std::vector<int> levelorder(tree *root){ std::queue<tree *> q; q.push(root); std::vector<int> vec; while(!q.empty()){ tree *node = q.front(); q.pop(); vec.push_back(node->value); if(node->left != nullptr){ q.push(node->left); } if(node->right != nullptr){ q.push(node->right); } } return vec; } //前序遍历 void preorder(tree *root){ if(root == nullptr){ return; } vec.push_back(root->value); preorder(root->left); preorder(root->right); } //中序遍历 void inorder(tree *root){ if(root == nullptr){ return; } inorder(root->left); vec.push_back(root->value); inorder(root->right); } //后序遍历 void postorder(tree *root){ if(root == nullptr){ return; } postorder(root->left); postorder(root->right); vec.push_back(root->value); } int main(){ tree *t0 = new tree(1); tree *t1 = new tree(2); tree *t2 = new tree(3); tree *t3 = new tree(4); tree *t4 = new tree(5); t0->left = t1; t0->right = t2; t1->left = t3; t1->right = t4; preorder(t0); for(auto &i : vec){ std::cout << i << " "; } std::cout << std::endl; vec.clear(); inorder(t0); for(auto &i : vec){ std::cout << i << " "; } std::cout << std::endl; vec.clear(); postorder(t0); for(auto &i : vec){ std::cout << i << " "; } std::cout << std::endl; vec.clear(); return 0; }使用数组表示二叉树: 用数组表示时,观察可知节点下标为 i 时,父节点下标为 (i - 1) / 2 左节点下标为 2 i + 1 ,右节点下标为 2 i + 2 依此规律我们可以使用数组表示出二叉树#include<vector> #include<iostream> std::vector<int> vec; int parent(int i){ return (i - 1) / 2; } int left(int i){ return 2 * i + 1; } int right(int i){ return 2 * i + 2; } void pretree(std::vector<int> &tree, int i){ if(i < 0 || i >= tree.size()){ return; } vec.push_back(tree[i]); pretree(tree, left(i)); pretree(tree, right(i)); } void intree(std::vector<int> &tree, int i){ if(i < 0 || i >= tree.size()){ return; } intree(tree, left(i)); vec.push_back(tree[i]); intree(tree, right(i)); } void posttree(std::vector<int> &tree, int i){ if(i < 0 || i >= tree.size()){ return; } posttree(tree, left(i)); posttree(tree, right(i)); vec.push_back(tree[i]); } int main(){ std::vector<int> tree(10); for(int i = 0; i < 10; i++){ std::cin >> tree[i]; } pretree(tree, 0); for(auto &i : vec){ std::cout << i << " "; } std::cout << std::endl; vec.clear(); intree(tree, 0); for(auto &i : vec){ std::cout << i << " "; } std::cout << std::endl; vec.clear(); posttree(tree, 0); for(auto &i : vec){ std::cout << i << " "; } std::cout << std::endl; vec.clear(); return 0; }参考文章